Wellness Essential: The Synbiotic Duo of Probiotics and Prebiotics | Trio Nutrition
The information in this article and throughout Trio Nutrition’s blog is for informational purposes only, and should never be mistaken for professional medical advice.
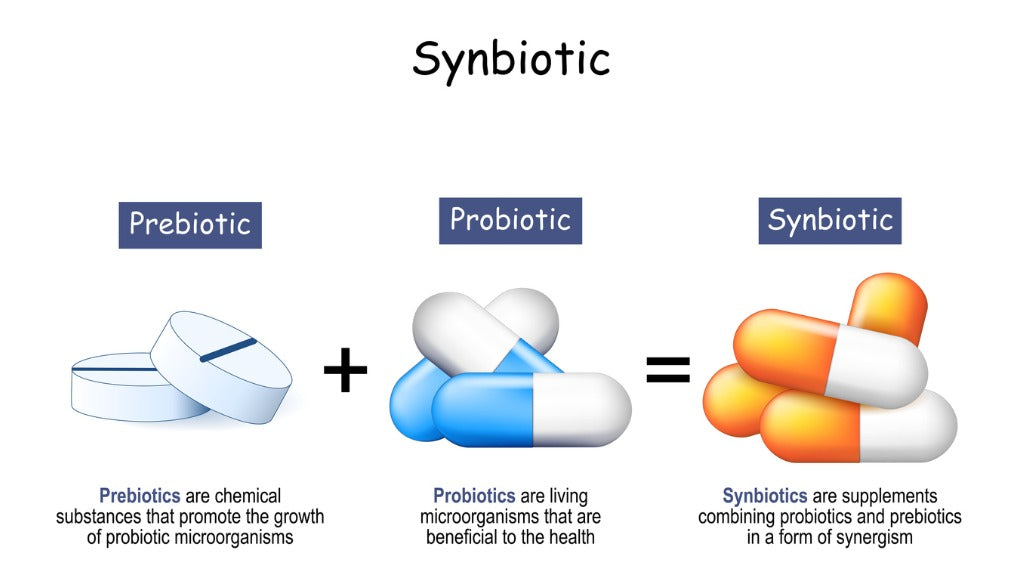
Synbiotic Defined
Before we begin, let’s define the term Synbiotic. Synbiotic specifically refers to a relationship between two different organisms in which one organism provides food or nutrients for the other organism, and the other organism provides some benefit to the first organism. This is a type of symbiotic relationship that is often seen between probiotics and prebiotics.
Historical Perspective
The journey of probiotics and prebiotics, often referred to as the dynamic duo of digestive and immunity wellness, is a tale of two vital components in the intricate world of gut health. Both these entities, though distinct in their roles, share a long history entwined with their significance in maintaining a harmonious balance within our bodies.
Probiotics, the beneficial bacteria residing in our gut, have been part of human existence since time immemorial. The use of fermented foods like yogurt and kefir can be traced back to ancient civilizations. These early cultures intuitively recognized the positive impact of these live microorganisms on digestion and overall well-being. In the modern era, scientific research has unveiled the profound influence of probiotics on our gut microbiome, shedding light on their role in supporting a robust immune system and promoting digestive health.
Prebiotics, the lesser-known but equally essential counterpart, have a history interwoven with dietary fiber. These indigestible components found in foods like garlic, onions, and asparagus serve as nourishment for probiotics. Although the term "prebiotics" was coined in the early 21st century, the concept of feeding beneficial gut bacteria has been an integral part of traditional diets worldwide. From the inclusion of fibrous root vegetables in the diets of ancient civilizations to the present-day emphasis on dietary fiber, prebiotics have played a silent but crucial role in promoting gut health.
Sources of Probiotics from Food:
Probiotics are abundant in various fermented foods, each containing different strains of beneficial bacteria. Here are some of the primary sources of probiotics from food:
- Yogurt: Yogurt is one of the most well-known probiotic-rich foods. Look for labels that mention live and active cultures, such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum.
- Kombucha Tea: Kombucha Tea is an effervescent beverage that is rich in probiotics, particularly strains of lactic acid bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and yeast like Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Kombucha is made from sweetened tea, typically black or green tea, and sometimes herbal teas. The sweetened tea serves as the substrate for fermentation. Kombucha offers the benefits of probiotics along with the potential advantages of antioxidants and organic acids, making it a popular choice for promoting gut health and overall well-being.
- Kefir: Kefir is a fermented milk drink similar to yogurt but with a thinner consistency. It contains a variety of probiotic strains and is an excellent source of probiotics.
- Sauerkraut: This fermented cabbage dish is rich in Lactobacillus bacteria. It's a common condiment in many European cuisines.
- Kimchi: A spicy fermented cabbage dish originating from Korea, kimchi is rich in probiotic bacteria, including Lactobacillus kimchii.
- Miso: A traditional Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans, miso is a source of the probiotic Bacillus subtilis.
- Pickles (fermented in brine): Pickles fermented in brine, rather than vinegar, can be a source of Lactobacillus probiotics.
- Tempeh: This fermented soybean product contains the probiotic strain Bacillus coagulans and is a popular meat substitute in vegetarian diets.
- Traditional Buttermilk: The traditional buttermilk (cultured buttermilk) made from the liquid leftover after churning butter contains probiotic cultures.
- Fermented Cheeses: Some types of cheese, like Gouda, cheddar, and Swiss, contain probiotic strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- Fermented Soy Products: Products like natto (fermented soybeans) and soy sauce, when traditionally fermented, can contain probiotic bacteria.
Sources of Prebiotics from Food:
Prebiotics are essentially fiber-rich foods that feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Incorporating these foods into your diet helps nourish the probiotics and support a healthy gut microbiome:
- Garlic: Garlic is a potent source of prebiotics, particularly inulin, which is known to support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Onions: Onions contain prebiotic fibers that stimulate the growth of good gut bacteria. These fibers are also responsible for the distinct flavor of onions.
- Leeks: Leeks are a member of the onion family and provide prebiotic fibers that help maintain a healthy gut environment.
- Asparagus: Asparagus is rich in prebiotic fibers like inulin, making it an excellent choice for promoting a healthy gut.
- Bananas: Unripe (green) bananas contain resistant starch, a type of prebiotic fiber that is an excellent food source for probiotics.
- Chicory Root: Chicory root is one of the richest natural sources of inulin, a well-known prebiotic fiber.
- Jerusalem Artichoke: Jerusalem artichoke, also known as sunroot or sunchoke, is another high-inulin root vegetable.
- Dandelion Greens: These bitter greens contain prebiotic fibers that can support gut health and digestion.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats, barley, and wheat contain prebiotic fibers and are valuable additions to a gut-healthy diet.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only excellent sources of plant-based protein but also provide prebiotic fibers that support gut bacteria.
The Symbiotic Connection is Synbiotic
The terms "symbiotic" and "synbiotic" are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference between the two.
Symbiotic refers to any relationship between two different organisms in which both organisms’ benefit. This can include relationships between different species of animals, plants, or even microorganisms.
Synbiotic, on the other hand, specifically refers to a relationship between two different organisms in which one organism provides food or nutrients for the other organism, and the other organism provides some benefit to the first organism. This type of symbiotic relationship is often seen between probiotics and prebiotics.
Probiotics and prebiotics are a harmonious pair in the world of gut health. Probiotics are the live microorganisms that colonize our gut, while prebiotics are the food that nourishes and sustains these friendly bacteria. The synergy between these two is synbiotic and it forms the basis for a balanced and healthy gut microbiome.
Probiotics primarily consist of various strains of bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, as well as yeast like Saccharomyces boulardii. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. They help in digestion, nutrient absorption, and contribute to the overall health of our digestive system.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are typically non-digestible fibers that make their way to the colon, where they serve as nourishment for probiotics. By promoting the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria, prebiotics aid in maintaining a diverse and thriving gut microbiota. This diversity is key to a robust immune system, efficient digestion, and protection against harmful pathogens.
Chemical Structure and Forms
Probiotics come in various strains, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Common probiotic strains include Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Saccharomyces boulardii, among others. They are available in different forms, including capsules, powders, and fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kombucha tea and sauerkraut.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are primarily composed of dietary fibers such as inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS). These fibers are naturally present in foods like garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and chicory root. Prebiotic supplements are also available for those looking to boost their prebiotic intake.
The Importance of the Dynamic Duo
The combination of probiotics and prebiotics offers a range of health benefits when incorporated into your daily wellness routine:
- Improved Digestive Health: Probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, reducing the risk of digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diarrhea.
- Enhanced Immune Support: A healthy gut microbiome supported by probiotics and prebiotics is linked to a stronger immune system, helping your body fend off infections.
- Weight Management: Some studies suggest that the balance of gut bacteria influenced by probiotics and prebiotics can aid in weight regulation.
- Mood and Mental Health: The gut-brain connection is a growing area of research, and maintaining a healthy gut may positively impact mood and mental well-being.
- Nutrient Absorption: Probiotics play a role in nutrient absorption, ensuring that your body gets the most out of the food you consume.
- Protection Against Harmful Bacteria: Probiotics compete with harmful bacteria in your gut, reducing the risk of infections and foodborne illnesses.
Incorporating Probiotics and Prebiotics
To enjoy the full benefits of this dynamic duo, consider including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, Kombucha Tea, and fermented vegetables in your diet. Additionally, incorporate prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and asparagus to nourish these friendly bacteria.
For added convenience, high-quality probiotic and prebiotic supplements are available. It's time to seize command of your digestive health and explore the transformative potential of Nirvana Kombucha Multi-Strain Probiotics and Prebiotic formula by Trio Nutrition. Don't miss this opportunity to elevate your energy, banish bloating, enhance immunity, and rejuvenate your gut. Embark on your journey to a healthier, happier you today!
Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes or starting any new supplements. Personalized guidance can help you make informed choices that align with your unique health needs.
In conclusion, the dynamic duo of probiotics and prebiotics forms the foundation of a healthy gut, supporting digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. Whether obtained through dietary choices or supplements such as Trio Nutrition’s Nirvana Kombucha, their combined power can be a valuable addition to your wellness journey.
So, if you're looking to boost your digestive health and overall vitality, consider exploring the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics, the dynamic duo of gut wellness. Try Nirvana Kombucha by Trio Nutrition with our risk-free 60 day money back guarantee.

Leave a comment